In the field of project management particularly in the areas of software development and user experience design, Agile and Design Thinking are two well-liked methodologies. Both strategies seek to encourage creativity, teamwork and adaptability. They do, however have unique qualities and may be more appropriate for particular projects. This article will examine the subtle differences between Agile & Design Thinking and assist you in choosing the best strategy for your project.
Understanding Agile Methodology
An incremental and iterative approach to project management is the agile methodology. It places a focus on adaptability, ongoing improvement and the prompt delivery of functional software or goods. Agile allows teams to react to change quickly and effectively by segmenting a project into manageable chunks called sprints.
Key Principles of Agile
The following tenets serve as the foundation for agile methodology:
- Agile places a high value on team member collaboration & effective communication. It prioritises people and interactions over processes and tools.
- The primary emphasis is on delivering a functional product rather than extensive documentation and working software is prioritised over thorough documentation.
- Contract negotiation should be prioritised over customer collaboration: Agile encourages ongoing customer input and participation throughout the development process.
- Adapting to change rather than sticking to a plan: Agile embraces change as a way to enhance the result and meet changing requirements.
Agile Manifesto

Agile methodology is built on the principles of the Agile Manifesto. It highlights the following four principles:
- Persons and interactions rather than procedures & tools
- Functional software over thorough documentation
- Customer involvement during contract negotiations
- Adapting to change versus sticking to a plan
Frameworks for Agile

Agile frameworks come in a variety of forms including Scrum, Kanban and Extreme Programming (XP). These frameworks offer instructions and recommended techniques for applying Agile methodology to projects.
Understanding Design Thinking Methodology
A human centered strategy for innovation and problem solving is called design thinking. It focuses on comprehending user needs, investigating various viewpoints and coming up with original solutions. To achieve user-centric results, design thinking promotes empathy, experimentation and collaboration.
Key Principles of Design Thinking
The following principles serve as a guide for the design thinking methodology:
- Empathy: Understanding user needs, feelings and motivations in order to create effective solutions.
- Define: Clearly stating the issue at hand and specifying the desired result.
- Ideate: To come up with a variety of thoughts and options without bias or limitations.
- Prototype: Making a prototype allows for the collection of feedback and concept revision.
- Test: Prototypes are iteratively tested and improved in response to user input & insights.
Design Thinking Process
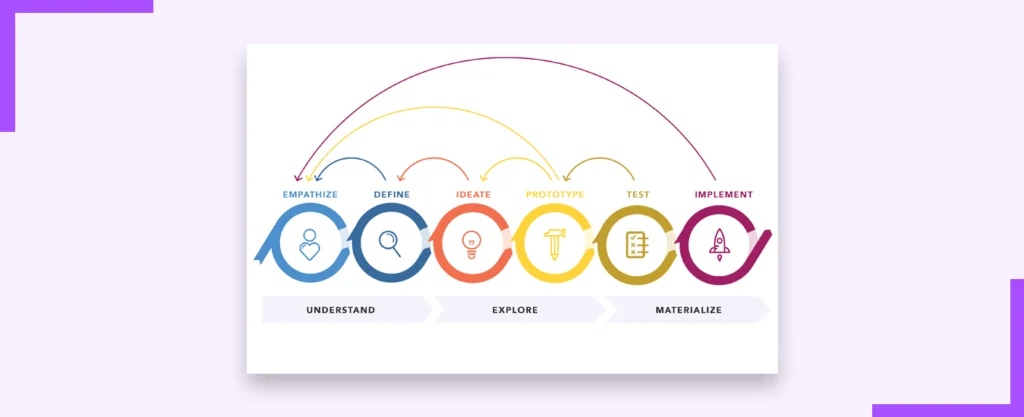
The Design Thinking process typically involves the following stages:
- Empathize: Understanding the users and their needs through research, interviews and observations.
- Define: Identifying the core problem to be addressed and establishing project goals.
- Ideate: Brainstorming and generating a multitude of potential solutions.
- Prototype: Creating low fidelity prototypes to visualize and test different ideas.
- Test: Gathering user feedback and refining prototypes to improve the solution.
Agile vs. Design Thinking
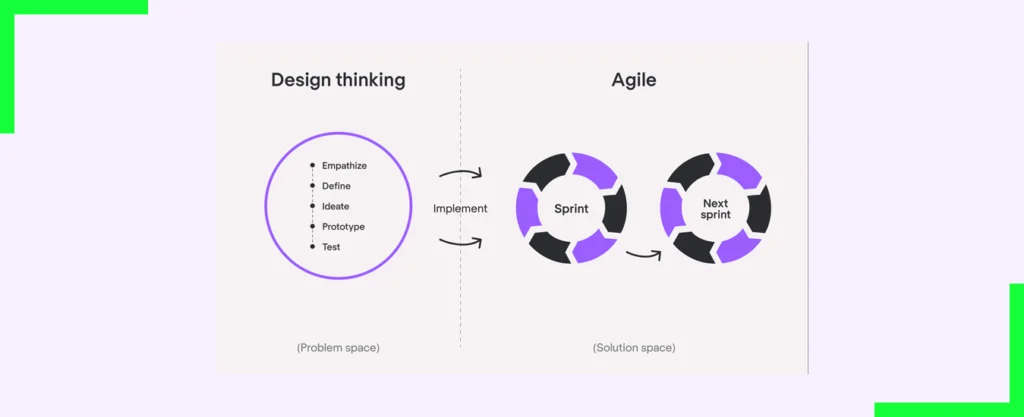
Although Agile and Design Thinking have some similarities like a focus on iterative development & collaboration they differ in their main objectives and methods of implementation.
Different Methods
Agile methodology is primarily concerned with producing products or software that function effectively and iteratively. It works well for projects requiring ongoing improvement and involving numerous stakeholders. Agile promotes flexible planning, open communication and regular feedback loops.
Design Thinking on the other hand places a strong emphasis on comprehending user needs and creating creative solutions. Empathy, creativity & experimentation are given priority in this more exploratory & human-centered strategy. In projects where problem solving, idea generation and user centric design are crucial, design thinking is particularly effective.
Similarities
Although Agile and Design Thinking have different methodologies they also have some things in common:
- Both methodologies encourage team members to work together and communicate clearly.
- They promote an attitude of constant learning & development.
- User involvement and feedback are prioritised in agile and design thinking methodologies.
- Both strategies place a high value on flexibility and adaptability in response to shifting needs or revelations.
Differences
Despite their similarities Agile and Design Thinking differ in their primary objectives and areas of focus:
- Agile methodology focuses on project management, delivery and iterative development whereas Design Thinking focuses on problem-solving and innovation.
- Agile is more structured and framework-oriented whereas Design Thinking is more fluid and adaptable.
- Agile teams work in sprints and deliver incremental results while Design Thinking involves iterative prototyping & refinement of solutions.
- Design Thinking places a stronger emphasis on empathy and user centric design compared to Agile.
Which Approach is Right for Your Project?

The best strategy for your project requires careful consideration of a number of factors. You can use the following important considerations to make an informed choice:
Project Goals
Take into account the size of your project and the precise results you hope to achieve. Projects that call for iterative development and frequent product releases are well suited to the agile methodology. On the other hand projects that require problem-solving, user research and ideation are best served by design thinking.
Team Membership
Analyse the knowledge and abilities of your team. Cross functional teams with a variety of skills are required by the agile methodology to ensure effective collaboration and development. A multidisciplinary team that can bring various viewpoints and ideas to the table is beneficial for Design Thinking.
Problem Complexity
Think about how difficult the issue you’re trying to solve is. Agile methodology might be more appropriate if solving the problem calls for a methodical and structured approach. Design Thinking can offer a useful framework for investigation & innovation for complex problems that call for user centric solutions.
You can decide whether Agile or Design Thinking is the best strategy for your unique requirements by carefully examining these factors and comprehending the particular requirements of your project.
Example for Agile vs Design Thinking
The Spotify brand:
In their product development process the well known music streaming service Spotify excels at fusing Agile and Design Thinking methodologies. Want to know how?
Agile Methodology: Spotify’s engineering teams iterate and improve the platform continuously through Agile sprints. Regular updates are made, user feedback is gathered and they adjust to changing trends & needs.
Design Thinking: Spotify’s culture is permeated with this concept. Through research, ideation and rapid prototyping they have a thorough understanding of user preferences. Their design choices are influenced by user feedback resulting in a unique and user friendly music experience.
Spotify maintains its responsiveness, innovation and user centricity by fusing Agile & Design Thinking. While Design Thinking ensures a thorough understanding of users and innovative problem solving their Agile approach enables effective development & adaptation.
Overall Spotify’s adoption of Agile and Design Thinking has helped the company become a leading music streaming platform by providing a customised music experience.
Conclusion
Both the Agile methodology and Design Thinking are potent methodologies that have specific benefits for various project types. Agile offers a structured framework for effective project management & iterative development whereas Design Thinking encourages creativity, empathy and user centric design. You can choose the strategy that best fits your goals and objectives by being aware of the differences between the two approaches and taking into account the particulars of your project!
Bridge the gap between project management & user centered design with YellowSlice! Book an appointment with the best UI UX design agency today.

FAQs about Agile vs. Design Thinking
Does Design Thinking work well with Agile?
Agile and Design Thinking can indeed complement each other well. While Agile provides a framework for iterative development and project management here on the other side Design Thinking offers a human centered approach to problem solving & innovation. User centric design & continuous improvement are made possible throughout the development process by integrating the two methodologies.
Can we implement parts of Design Thinking and still be successful?
Yes, you can use some aspects of design thinking and still succeed. The stages of design thinking include empathising, defining, ideating, prototyping and testing. Teams can choose and adapt particular phases or techniques from design thinking to improve their problem solving and innovation process depending on the project & its requirements.
Where does design happen in Agile?
Design is a continuous part of the Agile development process. Each sprint or iteration includes design activities that help the team address design related issues and come to wise decisions. During the planning fine tuning and implementation phases, agile teams collaborate on design elements to make sure that the design changes as the development does.
Is Design Thinking applicable to all problems?
Though Design Thinking can be used to solve a variety of issues its applicability will depend on the situation. Problems requiring user centric design, innovation and the exploration of new possibilities respond well to Design Thinking. However, other approaches to problem solving might be more suitable for issues that are extremely technical or specialised.