Creating a successful product requires in-depth research and data collection about what the users expect from it and the kind of experience they are having. This can be achieved through usability testing, an exercise of testing your product with real people by making them go through a list of tasks and observing their responses to them.
Behzod Sirjani, Founder, Yet Another Studio, expresses the importance of usability testing by saying, “Good usability testing takes a holistic look at the potential audience that you can serve and the ranges of intended and unintended uses of a product to understand how you’re enabling people to do what they want with your product while preventing misuse.”
The main purpose of usability testing is to understand if your product and its design are usable enough to let them complete tasks they wish to do. By gaining these insights, you can further enhance your product and the test results will help in the overall product development in the long run.
Our usability testing guide will provide in-depth information about the importance of usability tests, when you should conduct usability testing, what usability testing determines, and the overall benefits of usability testing. Read on:
What is Usability Testing?

Usability Testing is a way of knowing what the users of a product think about it. This is done by letting them finish a set of tasks and observing their experience. The main goal is to identify any problems regarding the usability of the product and collate data and statistics to determine the user’s satisfaction levels with the product.
While usability testing’s primary motive is to test the usability and functioning of a product, its benefits go way beyond that. It also helps you understand the use cases of the product, get a better understanding of what your customers are thinking/expecting, and develop a fully-rounded product.
As Claire Marie Karat, Principal Consultant at the Karat Consulting Group says, “Usability cost-benefit data shows that including usability in product development actually cut the time to market and increases sales because usability and ease of use build quality into products and catch many expensive problems early on in the cycle when they can be addressed at a lower cost. Finally, working with users from the beginning of a product cycle ensures that the product is being designed so that users will be satisfied.”

How usability testing differs from traditional testing (bug or acceptance testing) is that it is done with real users or customers of the product. Since traditional testing is mostly done either by developers, designers or project managers, it could bring in an element of bias. This is not the case with usability testing as it is done by collecting real feedback from actual users.
History of Usability Testing
Usability testing has its origin in the human-centered approach to design This style of design was developed and established by IDEO that keeps the user at the center of all design processes. This method takes several qualitative and quantitative approaches like ideation, prototyping, purpose framework, etc. into consideration for creating user-centric products.
The approach to usability testing that is prevalent today took shape in the 1980s when personal computers were becoming more common. Since this was a new technology and only a limited number of users has access to computers, it was important to make them more usable and intuitive. To achieve this, programmers needed a deeper understanding of users’ thought processes for completing a task.
Through the years, important determining developments like research titled Verbal Reports as Data by Karl Ericsson and Herbert Simon made open opinions of users more popular.
Later, usability was defined by ISO 9241 as “the effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction with which specified users achieve specified goals in particular environments.”
These developments emphasized the usage of data from real users about their experience of using a product in product development. This was a significant shift from guessing how users were reacting to a product, to giving companies more concrete information about how to make their products better. This evolved into today’s usability testing.
Types of Usability Testing
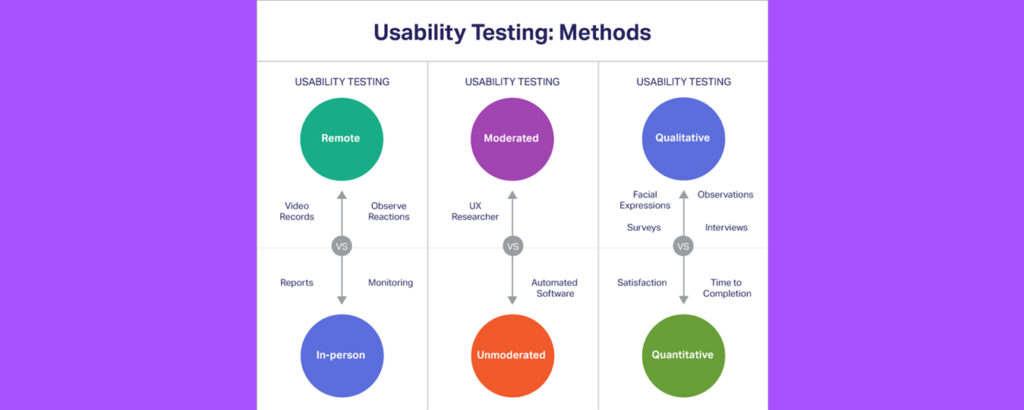
Understanding users’ specific needs and pain points are two of the main goals any company strives to gain. This is why usability testing has gained such an enormous amount of popularity as it derives exactly the kind of understanding that helps companies create better products.
Companies take different approaches to gain this understanding through different types of usability testing. Here are the main usability testing methods:
Qualitative and Quantitative:
Any kind of user research either falls into qualitative or quantitative usability testing. The one factor that separates these two approaches is the data they deal with. Qualitative analysis emphasizes the uses of words and meaning to understand the ‘why’ while quantitative methodology looks at the numbers and statistics to understand the ‘what’, ‘where,’ and ‘when’ of it all. Which methodology will prove to be a better bet for you will depend on your research goals.
Moderated and Unmoderated:
Every approach either falls under the moderated or unmoderated category. While the goals of moderated versus the unmoderated are more or less the same, where the two approaches differ is because of the presence of a moderator (facilitator) and environment-changes in certain cases.
Remote and In-Person:
What kind of product you are testing will determine whether you must choose to go with in-person or remote usability testing. If it’s a physical product, then in-person usability testing should be the obvious choice, whereas online tools like software can be done through remote usability tests.
In some cases, both remote and in-person usability testing might work. In this case, you must weigh the pros and cons of both and then decide which method you wish to pick.
Is Usability Testing different from User Testing?
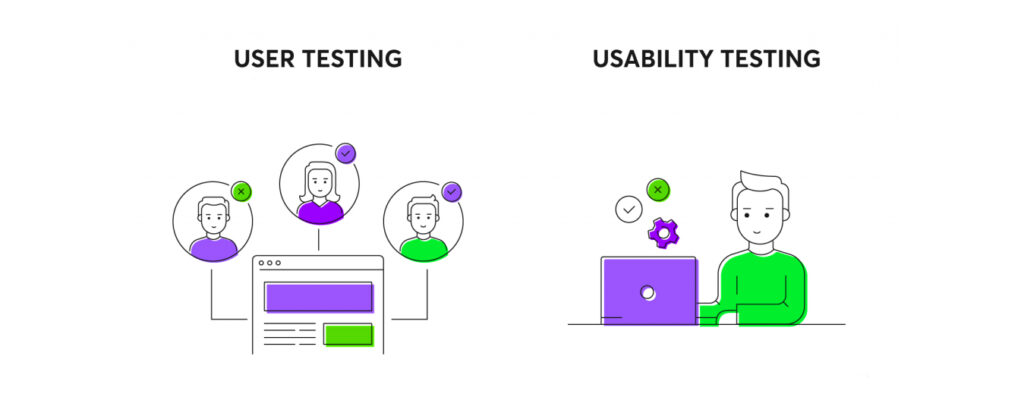
Both these approaches involve designers and users. What differentiates the two is their purpose. User testing determines whether there is a need for the product in the market and whether it will be in demand in the future. It is also used by marketers to test and understand the target audience and their needs.
Usability testing, on the other hand, can be done at just about any stage of the product development cycle by testing prototypes and wireframes. It also happens every time a product is re-developed. The main aim of usability testing is to know how the users are using the product and whether they are able to successfully complete tasks that they use the product for.
Usability Testing – What It’s Not
Usability testing is not just about gathering important information and user opinions about a product. It is a lot more than that. It shapes what a product would look and perform like in the future. There are several other techniques for testing products, but they are not as deep and effective as usability testing in bettering a product. These include:
A/B Testing:
This testing is done to determine which changes in design enhance product performance. Whereas usability testing observes user behavior and explains why a product variation is better than the previous one.
Surveys:
Surveys can be used to understand user behavior, just like usability testing. However, surveys don’t give out any insights about users’ actions in real time, falling short of what usability testing can provide.
Focus Groups:
Focus group discussions instigate sharing of behavior, preferences, and experiences of a product from a group of people. The aim is to gather opinions about a product and not know how it is used.
Advantages of Usability Testing

Having negative impressions about a product or usability problems can potentially damage its future usability. This is why companies resort to usability testing as it helps them improve product design and usability. When you employ usability testing, it not only improves the overall product but also provides several other benefits.
As Behzod Sirjani puts it, “Usability testing is important because as much as we like to believe that we are building products for ourselves, each person is unique. We’ve all had unique backgrounds, lived experiences, perspectives, preferences, and abilities. All of these things influence how we understand, approach, and experience a product.”
Let’s look at them individually.
Better Experience and Higher Conversion:
A great user experience amounts to conversion as customers would want to use a product they like. This is where usability testing comes into the picture. It helps makers identify how easy the steps are for the users to complete a task while using their products.
If there are too many steps to achieving the goal, or if they are too tough or complicated, the users will not prefer the product. Usability testing provides the answers to these significant questions and provides a possible solution, making your product more desirable.
Time Saving:
Usability testing helps companies realize bugs and other defects in the design and usability, giving them enough time to fix things before it’s too late. Fixing whatever issues a product has during the developmental stage is a lot less expensive and time-consuming. If such issues arise after the product has been launched, it can not only become an expensive proposition to pull off the product from the market and relaunch it after fixing the issues, but it can also damage the prestige of the company.
Creates Better Products:
Usability testing is an ongoing process that helps in knowing how the users are interacting with them. These insights provided by the users help companies improve products and create better products. By conducting usability testing, you can find out issues with design, layout, user errors, complicated steps and processes, and other errors.
As Shopify reported that one of the most common reasons a user leaves a shopping cart midway is due to a complicated check out process. Such challenges can be controlled through usability testing.
Taylor Palmer, Product Design and Lead at Range sums it up perfectly, saying, “Usability testing is one of the most fundamental ways to test the success of a design. Ensuring customers can find, understand, and use a solution contributes to the overall success of a product and business.”
When to Run Usability Testing
Designing and developing a perfect product is an evolving process that requires testing and redeveloping the same design several times over. During the course of the overall product development process, usability testing can be done multiple times to achieve a perfect design. Below are some general guidelines that will help you decide when you should run usability testing.
Before the Designing Process starts:
Opting for usability testing before you start redesigning a product is a great choice. If you have felt the need to redesign a product, it means there are things that are not working. In this case, doing usability testing will highlight the pain points and areas that require focus.
If you are beginning the development of a product from the scratch, use a competitor product to see how users are responding to it. These insights can then be used in your product development cycle.
When Your Prototype is Ready:
Once you have the prototype of the product ready, you can immediately run a usability test to understand where it stands in achieving the perfect product stage. This is called formative testing and it helps in consolidating your ideas so that you don’t reach the final stage of product development without any user feedback.
Talking about the importance of usability testing at a prototype stage, Vaida Pakulyte, UX Researcher and Designer, Electrolux, says, “I try to test at an early concept phase when I have a low fidelity wireframe to get some early input from real users. Once we get the first results, it’s important to use those results throughout other design phases and re-test with users.”
Before the Product Launch:
This is the most obvious and important stage in a product development cycle. You would want to get feedback from real users just before you launch your product so that you can fix whatever glitches, errors, shortcomings, etc. your product has. This type of testing is called summative testing, where you evaluate your product at the final stage to prevent any major mishap in its functioning.
The idea here is to get a large sample size so that you have comprehensive feedback to evaluate your product. This data can be benchmarked against all other feedback you have gathered during the early stages of product development.
Regularly After Product Launch:
There is always a scope to get better, and the same is true for your product usability as well. With time, user expectations might change, their user experience might go through a transformation and your product might require upgrades. Regular usability tests after the product has been launched will help you keep it upgraded and relevant.
Industry Best Practices for Usability Testing

“These days it’s pretty easy to make new products. There are a lot of frameworks and tools out there, but it’s still really hard to make a great product, a product that people can understand and use, a product that makes people feel good,” opines Aaron Walter, author of Designing For Emotion. To develop such a product, you not only need to understand what the users expect from it but also need to follow industry best practices to ensure that every step is formalized and perfected to ensure a great product.
Here are some best practices for usability tests that will allow you to ace your game.
Get Users on the Same Page:
User data, information and feedback are sacrosanct information and you must have their consent when you run the usability test. This must be done at the beginning as well as at the end of the test. You should not only ask for their consent to record the test and the corresponding results but also get their consent to keep the data.
Test a Wide Variety of Users:
Usability testing must be done with users from varied backgrounds who can bring different perspectives to your product. People from different backgrounds, demographics, experiences, expertise, abilities, markets and user behaviors must be included in usability testing. This will help you develop a well-rounded product that appeals to a wide range of users.
Opt for a Pilot Test:
It is always a good idea to run a pilot test with users from within your organization so that obvious pain points and other aspects can be identified and rectified even before you interact with real users. This will give you a chance to address more specific aspects of product usability without overburdening your users.
Have a Clear Evaluation Process:
Having a set evaluation process always helps in implementing a seamless testing process. Rushing through an unorganized approach after you have run the usability test will never yield the right results.
Keep it Short and Simple:
No matter how important running a usability test is for you and your brand, real users don’t have a lifetime to spend long hours giving you their feedback. So, keep your tests short and simple. If needed, you can have multiple shorter tests for the users so that they can finish them off in a quick time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Usability Testing
What is usability testing?
It is a technique of testing your product by asking real users to complete a list of tasks and noting and observing their interactions. The main aim is to see whether your product lets them achieve their goal with ease and what changes are required to let that happen.
How is usability testing done?
The ideal way to start with usability testing is to have a clear script. Outline your goals, the type and number of users to participate in the test, and the tasks you want them to complete. A clearly defined usability test will give you the right feedback. Anything that is too long, complicated and dull will not interest the users to provide their honest feedback.
What are the main aspects of usability testing?
The main aim is to improve the usability of a product. The test is taken by real users, they are asked to do real tasks, the feedback and response are observed and recorded by the researchers, the recordings and problems are analysed, and changes are recommended on the basis of the findings.
When should I run a usability test?
Although usability testing must be done throughout the developmental stages of a product, the best time to do it is before finalizing or launching a product. It should also be done before any redesign, during product iteration, and even after product launch. Running usability testing at different stages will help you develop a perfect product that is devoid of errors.
What are the types of usability testing?
Usability testing is classified into three types – moderated versus unmoderated, in-person versus remote, and explorative versus comparative.
How are user testing and usability testing different?
Although both terms are quite frequently used interchangeably, it is the aim of these two tests that differentiate them. While user testing is to identify whether your product will be in demand in the future, usability testing determines how easy is it for the customers to use your product and achieve their goals.
Usability testing is one of the most important aspects of developing a perfect product. It lets you find where your product lacks and how it can be improved in providing the users with a great experience and helping them achieve their goals.
The UX/UI of any product has become an extremely important aspect of any product and striving to design a product that provides the best user experience is something every brand must do. Conducting usability testing, a task that determines the success of your product, must be handled with professionals who excel in the task, and YellowSlice is one such professional design consultancy that emotes and innovates to deliver an unparalleled human experience.
So, if you wish to conduct usability testing, Contact Yellow Slice for the best-in-industry expertise.
![What is Usability Testing? [with use cases] What is Usability Testing?](https://www.yellowslice.in/bed/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/What-is-Usability-Testing.webp)



